Work Sampling Method (WSM)
The Work Sampling Method is an analytical technique used primarily in operations and industrial engineering
to assess the proportion of time spent on different activities within a workflow. Unlike continuous monitoring, work sampling involves taking random samples to estimate how workers allocate their time across various tasks. This method provides a snapshot of how effectively time is used, offering insights into productivity and areas for improvement.
The importance of the Work Sampling Method in modern business environments cannot be overstated. As industries strive for peak efficiency and optimal resource allocation, understanding how time is spent on the work floor becomes crucial. This method not only highlights inefficiencies but also supports better labor distribution and process improvement. It’s a vital tool in operations management and industrial engineering, helping businesses to scale efficiently while managing costs.
In this blog, we’ll look into the numerous benefits of work sampling, guide you through the work sampling procedure, and outline effective steps to implement this technique. We will also share some best practices to ensure that you get the most accurate and actionable results from your work sampling studies. Whether you’re new to this method or looking to refine your approach, this blog will provide valuable inquiries and practical advice to improve your operational strategy.
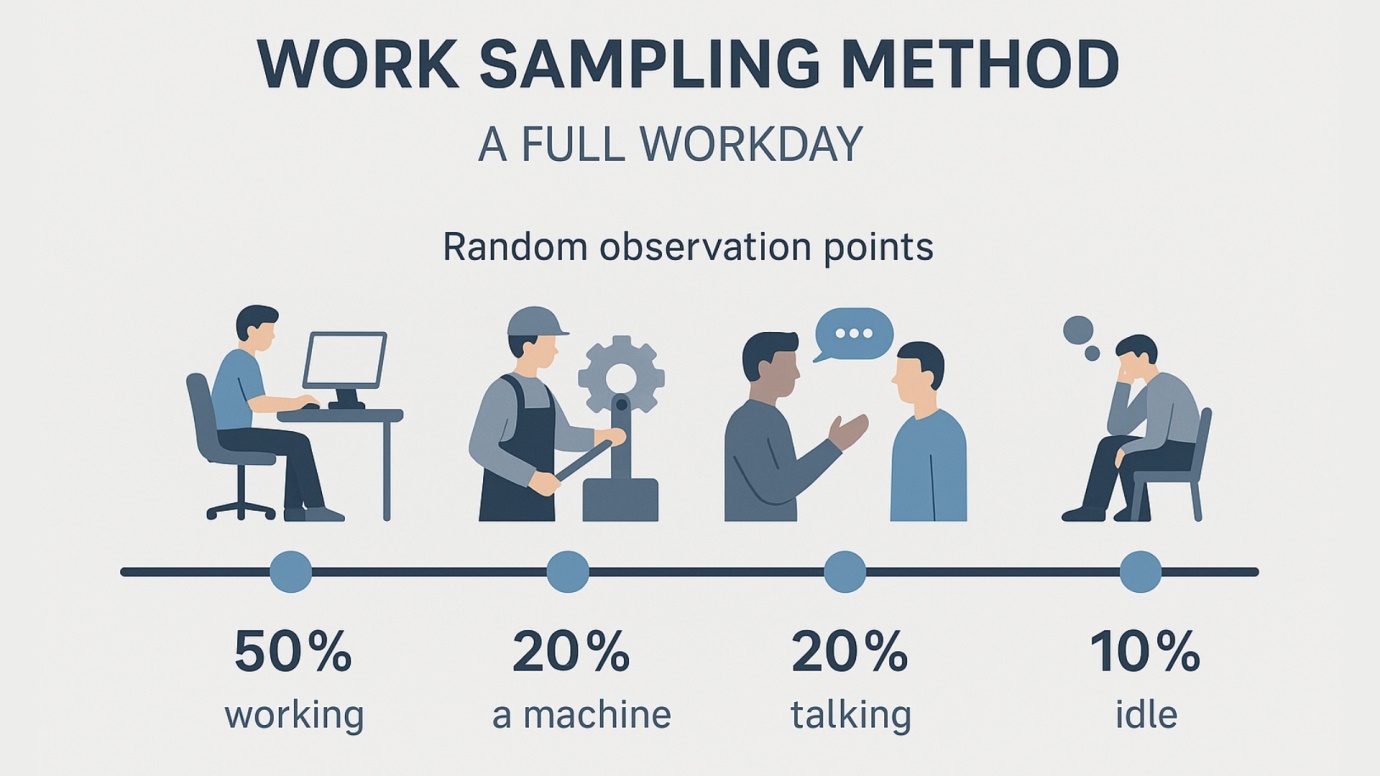
Understanding the Work Sampling Method (WSM)
Work sampling, also known as activity sampling or random sampling, is a technique used to analyze the proportions of time devoted to various tasks within a specific period. This work sampling method involves observing random intervals to estimate how much time employees or machines spend on different activities. It is especially prevalent in operations management and industrial engineering, where precise data on process efficiency and worker activity are critical.
The work sampling method has a rich historical background, dating back to the early 20th century. Initially developed by L.H.C. Tippett in the 1930s, the technique was refined and popularized by industrial engineers to simplify the labor-intensive process of continuous time studies. Over the decades, work sampling has evolved, adapting to the complexities of modern industrial operations and incorporating technological advances to improve data accuracy and applicability.
The key principles of work sampling revolve around the statistical theory of random sampling. This technique does not require continuous observation; instead, it collects snapshots of activity at random intervals, which statistically represent the distribution of various tasks over time. This method is highly effective in identifying non-productive time and determining workforce efficiency, making it a valuable tool in operations management.
Work sampling differs from other productivity measurement techniques, such as time studies, in several significant ways. While time studies involve continuous observation and recording of all tasks a worker performs, work sampling is less intrusive and less time-consuming, focusing on intermittent snapshots rather than continuous monitoring. This not only reduces the observer effect—where workers might alter their behavior because they know they are being watched—but also allows for larger scale studies involving more workers or longer observation periods without the corresponding increase in effort or cost.
In summary, work sampling is a scientifically validated, efficient, and effective method to gauge productivity and identify opportunities for improvement in various industries. Its application across diverse fields underscores its adaptability and the substantial benefits of work sampling in enhancing operational efficiencies and optimizing workforce performance.
Benefits of Work Sampling Method (WSM)
The Work Sampling Method offers a number of advantages that make it a preferred choice for many businesses seeking efficiency and productivity improvements. This technique stands out for its cost-effectiveness, minimal disruption, statistical reliability, and versatility, proving beneficial in a range of industries.
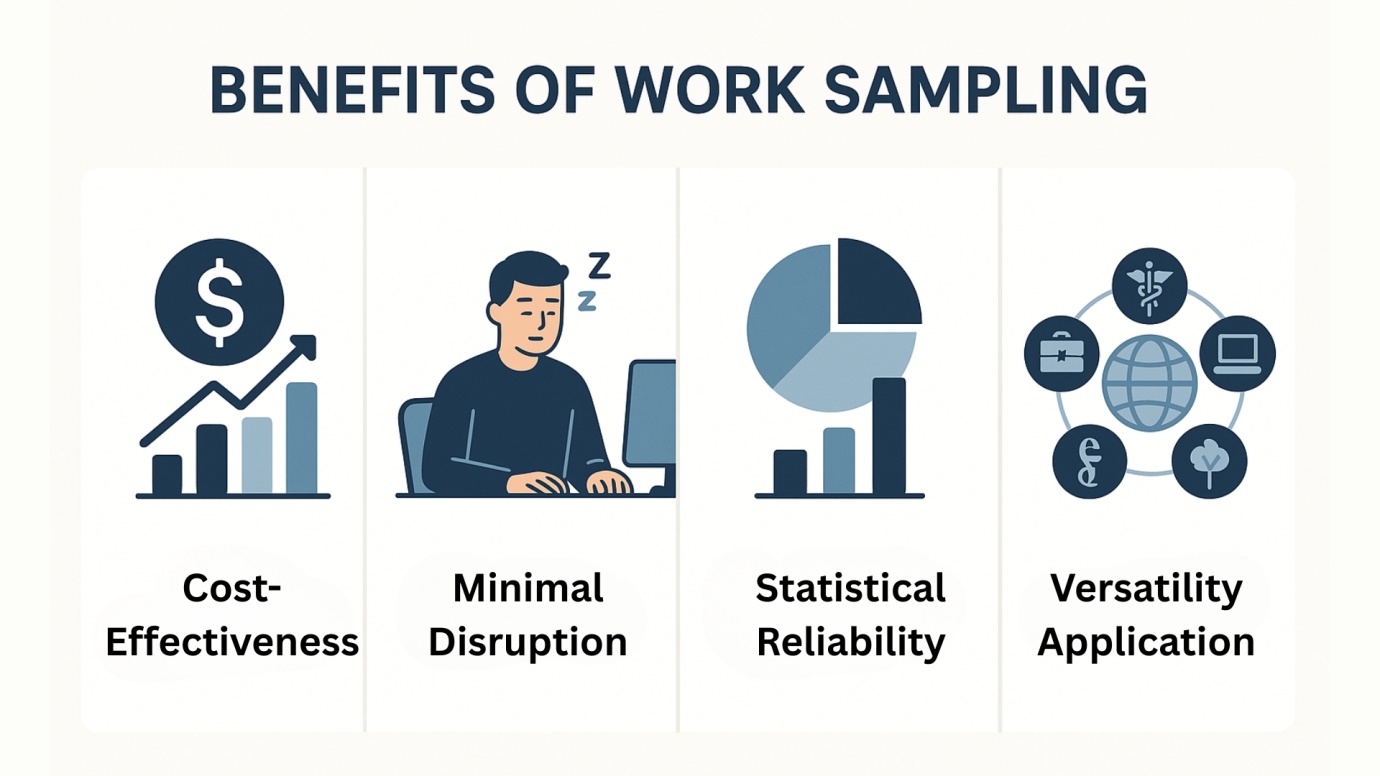
- Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Continuous Observation: One of the most significant benefits of work sampling is its cost-effectiveness. Unlike continuous observation methods, which require prolonged periods of monitoring by highly trained personnel, work sampling involves capturing data at random intervals. This strategic reduction in data collection reduces the manpower and hours needed, dramatically lowering the costs associated with labor and operational disruption. Organizations can conduct thorough work sampling procedures without the extensive resource allocation typically required for full-scale time studies, making it an economical alternative for budget-conscious operations.
- Minimized Disruption in the Workplace: Work sampling is designed to minimize disruption in the workplace, a critical factor for maintaining normal operations during the study period. Since observations are made at random and infrequent intervals, the presence of observers is less pronounced, and employees are less likely to feel the pressure of being watched continuously. This aspect of work sampling not only helps in capturing more accurate representations of typical work behaviour but also reduces the observer effect, leading to more genuine data collection.
- Statistical Reliability of Data: Despite the seemingly sporadic nature of work sampling, it provides statistically reliable data. The method relies on the principles of random sampling, which, when executed correctly, ensure that the observations are representative of the overall activity. This statistical grounding allows work sampling in operations management and industrial engineering to provide insights that are both accurate and scalable, supporting strategic decisions across various levels of management.
- Versatility across Different Industries: The versatility of the work sampling method is another compelling benefit. It can be applied in diverse settings—from manufacturing floors to office environments, healthcare facilities, and even remote work scenarios. This adaptability makes work sampling an invaluable tool for any industry looking to improve efficiency and better understand employee engagement with tasks. The ability to customize the implementation of work sampling techniques to suit specific industry needs or particular operational nuances further enhances its applicability and effectiveness.
The benefits of work sampling extend beyond simple time management to provide a comprehensive tool for operational improvement. Its cost-effectiveness, minimal workplace disruption, reliable data, and industry versatility make work sampling a crucial strategy for businesses aiming to optimize productivity and drive continuous improvement.
Preparing for Work Sampling
Effective preparation is critical to the success of any work sampling study. Proper planning not only enhances the efficiency of the process but also ensures that the data collected is both relevant and actionable. This section covers the essential steps of setting clear objectives, designing the study, and selecting the appropriate tools and technology, which are foundational to a successful work sampling procedure.
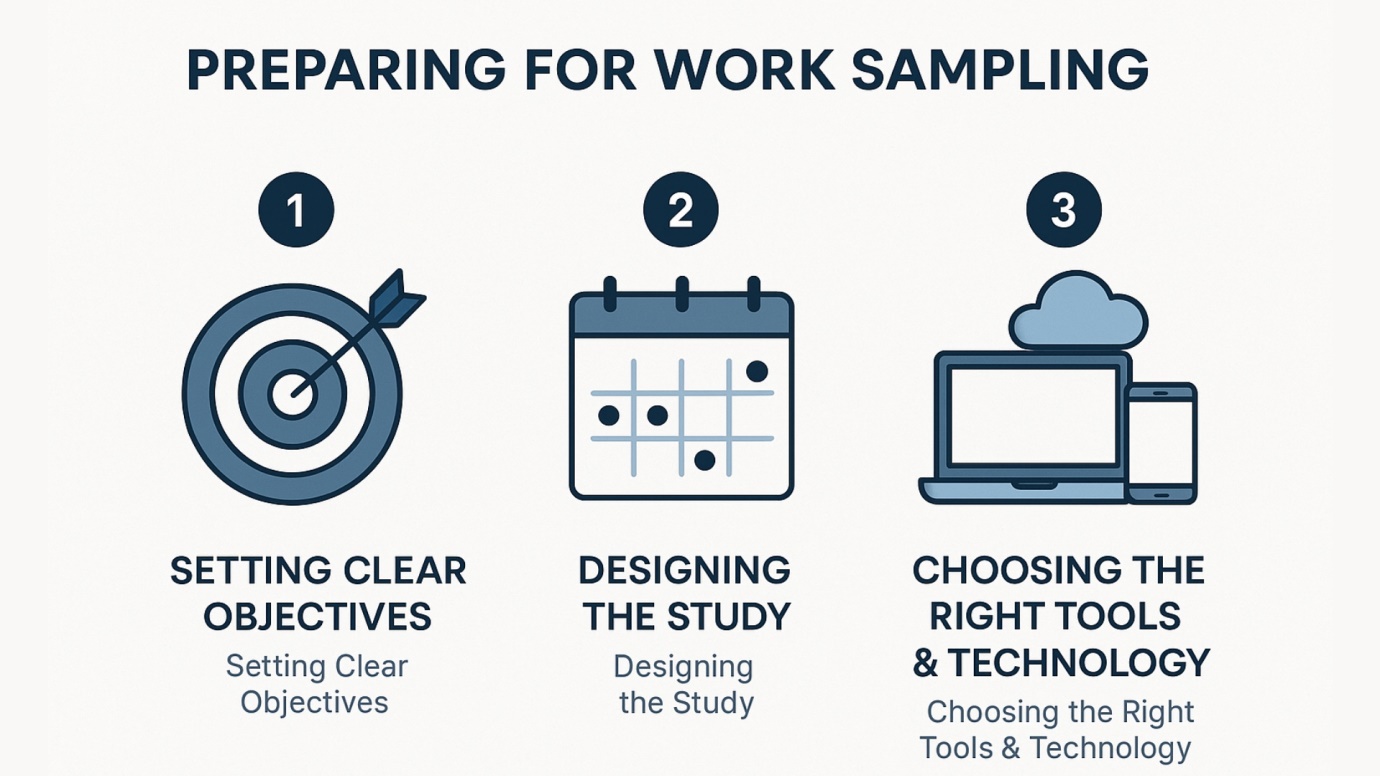
Setting Clear Objectives
- The first and foremost step in preparing for work sampling is to establish clear objectives. Understand what you aim to achieve with the work sampling method. Whether it’s identifying bottlenecks in production, measuring employee productivity, or assessing the frequency of certain tasks, having a well-defined goal will guide all other aspects of the study.
- Clear objectives help in focusing the study on specific activities or areas, ensuring that the efforts are concentrated and aligned with organizational goals. This clarity is vital as it directly impacts the relevance of the findings and the subsequent actions that an organization might take.
Designing the Study
- Designing the study is perhaps the most technical aspect of preparing for work sampling. This involves deciding how many observations are needed and at what times they should be made to statistically represent the work being analyzed. The design phase should consider the work cycles, peak periods, and potential variances in activity throughout the day or week.
- To determine the number of observations necessary, one must consider the desired confidence level and margin of error. These statistical parameters help in structuring a work sampling schedule that balances thoroughness with efficiency. Using work sampling techniques such as random sampling intervals can help in mitigating bias and ensuring that the data collected reflects typical operations, which is particularly crucial in industrial engineering and operations management contexts.
Choosing the Right Tools and Technology
- The effectiveness of work sampling greatly depends on the tools and technology used for data collection and analysis. Choosing the right tools involves selecting software and hardware that can accurately capture and analyze data with minimal intrusion. For instance, specialized work sampling software can automate much of the data collection and analysis, reducing the risk of human error and increasing the reliability of the results.
- Moreover, modern technologies such as mobile devices and cloud-based applications offer new possibilities for real-time data collection and analysis, enhancing the responsiveness and flexibility of the work sampling method. These tools not only simplify the process of recording and analyzing data but also enable easier sharing and collaboration across different departments or locations, which is beneficial for large-scale operations or companies with multiple branches.
In summary, thorough preparation in setting objectives, designing the study, and choosing appropriate tools and technology is crucial for increasing the effectiveness and efficiency of work sampling. Each step should be approached with a strategic mindset, ensuring that all aspects of the work sampling procedure are aligned with the overall business objectives and capable of providing insightful, actionable data.
Implementing Work Sampling Method (WSM)
Implementing work sampling effectively requires a structured approach to ensure that the data collected is accurate and the insights derived are actionable. This section provides a step-by-step assistance on conducting a work sampling study, from selecting tasks to be sampled to analyzing the collected data.
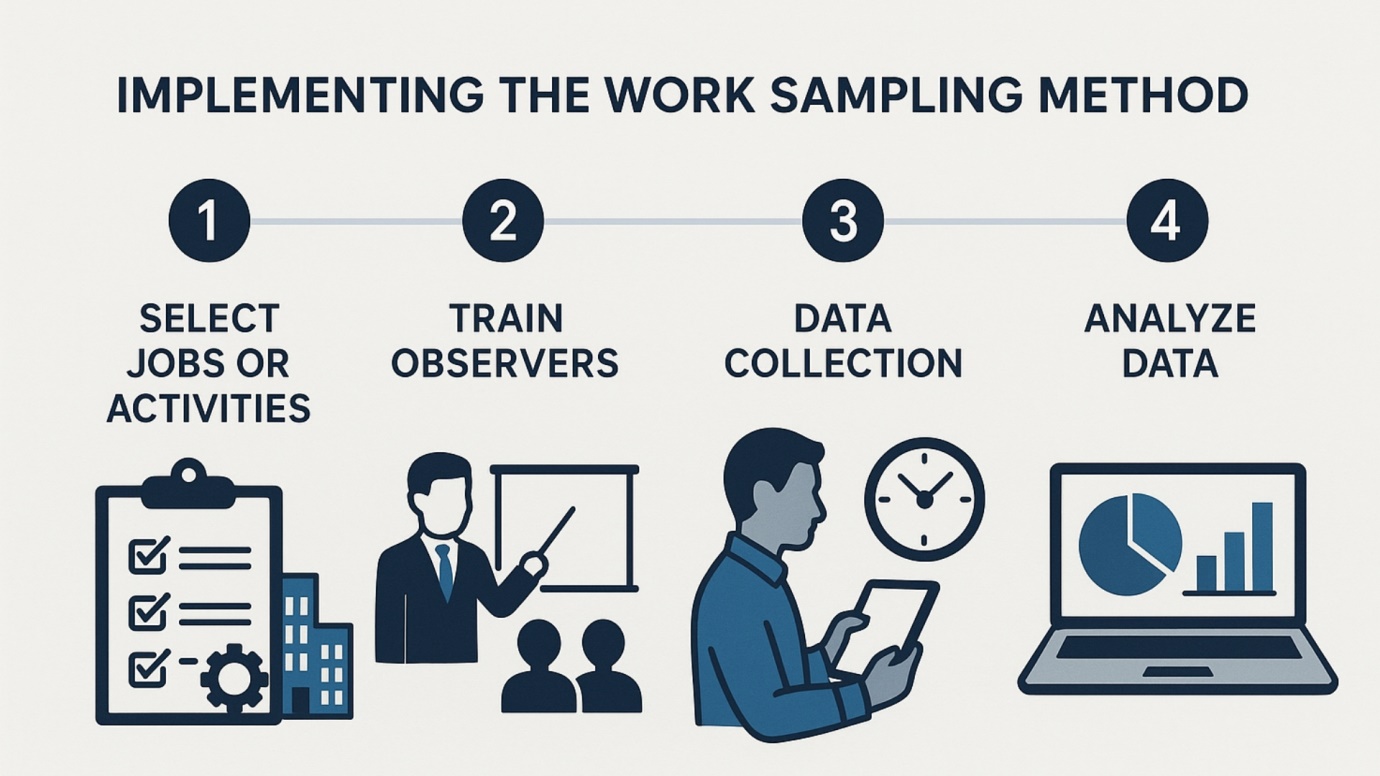
- Step 1: Selection of Jobs or Activities to Be Sampled: The first step in a work sampling method is to carefully select the jobs or activities that need to be sampled. This selection should align with the objectives set during the preparation phase. Focus on areas known for potential inefficiencies, or where there is little existing data on how time is spent. In contexts of operations management and industrial engineering, this might involve sampling a range of activities from machine operation to manual assembly tasks, ensuring a representative overview of various work elements.
- Step 2: Training Observers for Accurate Data Collection: Training observers is crucial to the success of the work sampling method. Observers need to understand not only what they are observing but also how to record it consistently. They should be familiar with the work sampling method and the specific criteria for recording data. Training should cover the purpose of the study, the importance of unbiased observation, and the use of any tools or technology deployed in the work sampling procedure. The more knowledgeable the observers, the more reliable the data collected will be.
- Step 3: Data Collection Methods: Data collection in work sampling involves observing and recording the occurrence of selected activities at random intervals over a specified period. Observers might use manual methods such as check sheets or leverage digital tools like apps or software designed for work sampling. The method chosen can significantly affect the efficiency and accuracy of data collection, so it's important to select tools that are easy to use and minimize errors in data entry.
- Step 4: Analyzing the Data: Calculating Ratios and Understanding Patterns: Once data collection is complete, the next step is to analyze this data to derive meaningful insights. This involves calculating ratios of time spent on different activities and identifying patterns that emerge from the data. For instance, if a significant portion of time is spent on non-value-added activities, it might indicate bottlenecks or inefficiencies. Analysis should focus on comparing the observed data against the set objectives to evaluate performance and identify areas for improvement.
Tips for Ensuring Accuracy and Consistency in Data Collection
To ensure the accuracy and consistency of work sampling data, consider the following tips:
- Maintain Randomness: Ensure that the timing of observations is random to avoid bias that could skew the data.
- Standardize Procedures: Develop clear, standardized procedures for observations to ensure that all data collectors operate in a consistent manner.
- Use Technology: Utilize technology to reduce human error and to handle data more efficiently and accurately.
- Regular Training: Offer regular refresher training for all observers to maintain a high standard of data collection quality.
- Pilot Testing: Conduct a pilot test to recognize any issues with the work sampling techniques or the particular setup, and make adjustments before full-scale implementation.
By implementing these steps and tips, organizations can implement the work sampling method effectively, leading to better understanding and management of workplace operations and productivity. This method, foundational in both operations management and industrial engineering, is crucial for organizations seeking to drive improvements through informed decision-making.
Analyzing and Using the Data
After collecting data through the work sampling method, the next important step is to analyze and interpret these findings to make informed decisions that enhance productivity and efficiency. This section covers how to interpret results from a work sampling study, the actionable insights that can be derived, and the process of making informed decisions based on this data.
How to Interpret Results from a Work Sampling Study
Interpreting results from a work sampling study involves several key steps. Initially, the data needs to be compiled and the proportion of time spent on various activities calculated. This is typically presented in percentage terms, illustrating how much of the total observation time was dedicated to specific tasks. These results should then be analyzed in the context of the study’s objectives to determine whether current performance aligns with expected productivity standards.
For effective interpretation:
- Compare the time distributions against benchmark or expected values if available.
- Identify any deviations from expected patterns which could indicate inefficiencies.
- Look for trends over time or differences among groups of workers, shifts, or departments.
Examples of Actionable Insights That Can Be Derived from the Data
The data collected through work sampling method can reveal a variety of actionable insights. For example:
- Time Allocation: Discover how much time is spent on value-added vs. non-value-added activities. This can highlight opportunities for process improvement or automation.
- Bottleneck Identification: Pinpoint stages in the process where delays consistently occur, indicating bottlenecks.
- Resource Utilization: Assess whether resources are being over or under-utilized, which could lead to adjustments in staffing or equipment allocation.
- Comparative Analysis: Evaluate performance across different teams or departments to identify best practices or areas needing additional training or support.
These insights enable managers and engineers involved in operations management and industrial engineering to make targeted improvements that can significantly affect operational efficiency and employee productivity.
Making Informed Decisions Based on Work Sampling Data
Making informed decisions based on work sampling data requires a strategic approach to implementing the insights gained:
- Prioritize Changes Based on Impact: Focus on changes that offer the most significant potential improvements in efficiency or cost savings.
- Implement Pilot Projects: Before rolling out large-scale changes, test improvements in a controlled environment to measure their impact and refine the approach as necessary.
- Continuous Improvement: Use work sampling as an ongoing tool to track the effectiveness of changes and continue refining processes over time.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Ensure that all relevant stakeholders are involved in the decision-making process to gain support and encourage adherence to new methods or processes.
By effectively analyzing and utilizing data from work sampling, organizations can not only improve their operational efficiency but also enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities. This leads to a more agile and responsive operational framework, crucial for maintaining competitiveness in today’s fast-paced business environments. Through detailed and continuous application of the work sampling method, businesses can ensure sustained improvements and a deep understanding of their operational dynamics.
Best Practices in Work Sampling
Implementing work sampling successfully requires adherence to established best practices. These guidelines help in maximizing the effectiveness of the work sampling method while ensuring ethical standards and accuracy. Here, we will explore the do’s and don’ts, common pitfalls, and the importance of maintaining ethical standards during observation.
Do's and Don'ts for Successful Work Sampling
- Do:
- Clearly Define Objectives: Before beginning a work sampling study, be clear about what you hope to achieve. This clarity will guide all aspects of the study, from the design to the interpretation of results.
- Train Observers Thoroughly: Ensure that all observers are well-trained and understand the work sampling procedure and the tasks they are observing. This training reduces observer bias and improves data accuracy.
- Use Random Sampling Techniques: To get unbiased results, use random sampling times throughout the workday. This helps in capturing a true representation of the activities being studied.
- Regularly Review and Adjust Sampling Methods: As the study progresses, review the data collection methods and make necessary adjustments to improve accuracy and relevancy.
- Don't:
- Overlook the Importance of Randomness: Skipping randomness can cause biased results that do not accurately reflect true working conditions.
- Disrupt the Workflow: Avoid altering the normal workflow of the employees being observed. The goal is to capture the genuine behavior and real conditions.
- Ignore Data Security: Be cautious with the data collected, ensuring it is stored and handled with high levels of security and confidentiality.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Several pitfalls can compromise the effectiveness of work sampling:
- Insufficient Sample Size: Too few observations can lead to inaccurate conclusions. Ensure the sample size is statistically valid to support reliable inferences.
- Observer Bias: Observers may influence or interpret what they see based on personal biases. To minimize this, provide comprehensive training and rotate observers if possible.
- Misinterpretation of Data: Without a proper understanding of the context, data can be misinterpreted. Engage with operational staff to gain insights and context that can inform accurate data interpretation.
To avoid these pitfalls, maintain rigorous standards in your work sampling techniques and continually assess the process for potential improvements.
Maintaining Ethical Standards During Observation
Ethical considerations are paramount in work sampling to protect the privacy and dignity of workers:
- Transparent Communication: Inform all participants about the nature, purpose, and procedures of the work sampling study. Transparency builds trust and cooperation.
- Respect Privacy: Ensure that the observation process does not invade the personal privacy of the employees. Observations should focus strictly on work-related activities.
- Voluntary Participation: Whenever possible, make participation in the study voluntary to uphold ethical standards and respect for individual choice.
By adhering to these best practices, you can make sure that your work sampling efforts are successful, ethical, and yield valuable insights that can significantly enhance work sampling in operations management and industrial engineering. These practices not only foster a culture of continuous improvement and respect within the workplace but also contribute to the overall effectiveness and accuracy of the work sampling procedure.
Future of Work Sampling Method (WSM)
As industries evolve and new technologies emerge, the work sampling method continues to adapt, promising even more efficient and precise studies in the future. This section explores current innovations and trends in work sampling methodology, the enhancing role of technology and software, and predictions for how work sampling will continue to shape the future workplace.
Innovations and Trends in Work Sampling Methodology
- Recent innovations in work sampling techniques have focused on integrating more sophisticated statistical tools and data analytics, which provide deeper insights and more predictive capabilities. Machine learning models, for instance, are being used to analyze large datasets collected through work sampling, enabling patterns and anomalies to be identified more quickly and accurately than ever before.
- Additionally, there is a growing trend towards the integration of work sampling with other observational methods, such as time-motion studies, to create a more comprehensive view of workplace efficiency. This extensive approach not only enhances the depth of analysis but also improves the actionable outcomes of work sampling studies.
The Role of Technology and Software in Enhancing Work Sampling Studies
- Technology and software play pivotal roles in modernizing the work sampling procedure. With the advent of IoT (Internet of Things) devices and wearable technology, data collection can be more continuous and less obtrusive, providing real-time insights into workforce activities without disrupting the natural work environment. These technologies ensure a higher level of accuracy and provide a wealth of data that can be used for more complex analyses.
- Software solutions designed specifically for work sampling are increasingly sophisticated, offering features such as automated data collection, integration with existing enterprise systems, and advanced data visualization tools. These features make it easier for businesses to implement work sampling in industrial engineering and operations management, facilitating better decision-making and strategic planning.
Predictions for Work Sampling in the Future Workplace
- Looking ahead, work sampling is set to become an even more integral part of strategic management in various industries. As workplaces become more digital and connected, work sampling will likely be increasingly automated and integrated with other data-driven business processes. This integration will help organizations to continuously monitor and optimize operations, not just as periodic reviews but as a part of everyday business practice.
- Furthermore, as remote work and flexible schedules become more common, traditional work sampling techniques will adapt to accommodate these new work arrangements. Expect future work sampling methods to leverage data from virtual work environments to analyze productivity and workflows in ways that were not previously possible.
In summary, the future of work sampling looks robust and dynamic, with advances in technology and methodology enhancing its effectiveness and applicability. As businesses continue to seek efficiency and productivity gains, work sampling will remain a key tool, evolving to meet the needs of modern, data-driven enterprises. By staying updated with these trends and innovations, companies can leverage the benefits of work sampling to maintain competitive advantage and build sustainable growth.
FAQs
A. The Work Sampling Method (WSM) is a productivity analysis technique that uses random observations to determine how time is allocated across different activities in an operation. This work sampling method provides valuable insights into workflow efficiency, identifies inefficiencies, and helps improve overall productivity.
A. Unlike continuous observation that requires constant monitoring, work sampling involves taking random, intermittent observations, making it less disruptive and more cost-effective.
A. The key benefits of work sampling include cost-effectiveness compared to full-time studies, minimal disruption of normal work activities, statistical reliability of data, and its applicability across various industries.
A. In operations management, work sampling is used to assess employee productivity, identify process bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation to enhance operational efficiency.
A. In industrial engineering, work sampling helps in analyzing manufacturing processes, improving layout designs, and ensuring that equipment and labor are being used efficiently.
A. Organizations can ensure data accuracy by training observers effectively, maintaining randomness in observation intervals, and using technological tools to automate and error-proof the data collection process.
A. Ethical considerations include ensuring transparency about the study’s purpose and procedures, respecting employee privacy by focusing only on work-related activities, and potentially making participation voluntary.
A. Emerging trends in work sampling include the integration of machine learning for deeper data analysis, the use of IoT devices for real-time monitoring, and broader applications across remote and hybrid work environments.
A. Yes, work sampling is versatile and can be effectively used in non-manufacturing environments such as services, healthcare, and IT, helping to analyze workflows and improve service delivery.
A. Work sampling provides empirical data that helps leaders make informed decisions about resource allocation, process improvements, and strategic planning, thereby driving better business outcomes.
A. It’s a technique that uses random observations to measure how time is spent on tasks, helping improve productivity and efficiency in industrial operations. You can learn more about our approach on our Industrial Engineering Services page.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have delved deeply into the work sampling method, highlighting its significance and diverse applications across modern business practices. We began with an introduction to work sampling, outlining its development, key principles, and distinct advantages over other productivity measurement techniques. Recognized for its utility in operations management and industrial engineering, work sampling provides a vital tool for measuring the allocation of time among various activities within an organization.

We discussed the numerous benefits of work sampling, which include its cost-effectiveness in comparison to continuous observation, minimal disruption to regular work processes, and the statistical reliability of the data collected. Such benefits underscore its versatility and applicability across different industries, from manufacturing to healthcare.
The process of preparing and implementing work sampling requires setting clear objectives, designing a thorough study, selecting the right tools and technology for data collection and analysis, and finally, understanding how to interpret and use the data effectively. The implementation phase involves a detailed step-by-step approach, ensuring accurate data collection, and subsequently analyzing this data to extract actionable insights that inform strategic decisions.
Best practices in work sampling emphasize maintaining ethical standards and avoiding common pitfalls, which are critical for the success of any work sampling study. Looking forward, the integration of advanced technologies and methodologies promises to enhance the efficiency and scope of work sampling further, making it an indispensable part of strategic management and operational improvements.
Work sampling is more than just a methodology; it’s a transformative approach that can profoundly impact how organizations view and optimize their workflows. By offering a means to scrutinize operations through a detailed and analytical lens, work sampling enables management to not only see their operations as a series of outputs but to understand and refine the web of interconnected activities for enhanced productivity and efficiency.
We encourage organizations to implement work sampling in their operational strategies. Whether your organization operates within manufacturing, healthcare, IT, or any other sector, work sampling can be adapted to meet specific needs and challenges, driving significant improvements in process efficiency and organizational success.
If you want to know more about our consultation services, visit our Home Page.

